Introduction
- General
- What is risk?
- 6 questions to define the project
- The key areas of concern
- What should risk analysis provide?
- 3 Ways to view risk management
- General comments on risk assessment
- Accountability
- General comments on planning
- What are the core process steps to assess a risk?
- Simple process outline
- What are the basic overall process steps?
- Stakeholders
- Success measures
- Why carry out Risk Assessment?
- Project Life Cycle
The Risk Management process
- General
- Define
- Identify the risks and responses
- Organise - prioritise risks and responses
- Ownership - risks, responsibilities and contractors
- Estimation
- Evaluation
- Planning
Risk issues
Modelling
Events
Networks and branching
Other
Risk management - Complex branching
© Copyright 2020 all rights reserved March Limited
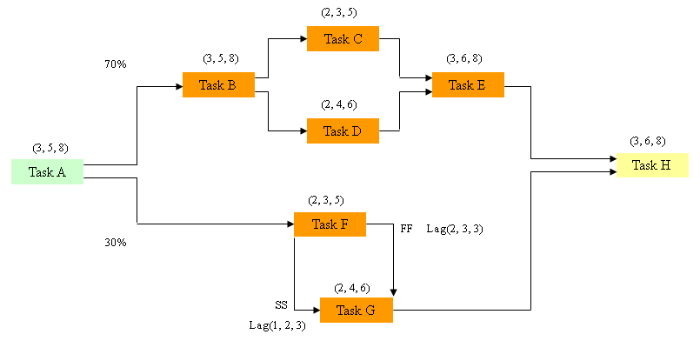
Complex branching
Following on from the simple case of branching [see simple branching], the above gives an example of a more complex model.
Here, as previously, we have 2 potential pathways with probabilities of 70% and 30%.
Within each of these one pathway has a simple activity network with simple finish to start dependencies, with Task C and Task D beginning at the same time.
The second pathway contains another simple activity network but one in which there is a lag in Task G.
The spreadsheet for this ‘complex branching’ example is next [see complex branching part 2].
other areas of interest in the series
- PRINCE2 2009PRINCE2 2009 updates PRINCE2 2005 and covers the principles, the themes -
business case, organisation, quality, plans, risk, change and progress.
The processes – starting up a project, directing a project, initiating a project, controlling a stage,
managing product delivery, managing a stage boundary, closing a project and tailoring PRINCE2 2009 and more... - PRINCE2 2005PRINCE2 2005 covers definition, terminology, the processes - Starting up a Project (SU), Initiating a Project (IP),
Directing a Project (DP), Controlling a Stage (CS), Managing Product Delivery (MP), Managing Stage Boundaries (SB),
Closing a Project (CP) and Planning (PL). The components – Business case, Management of risk,
Quality in a project environment, Configuration management Change control, Organisation, Plans and Controls.
Also, Product-based planning, change control technique and quality review technique and more... - Project managementProject management covers planning, milestones, objectives, scope, control, estimating, assumptions and constraints, problem statements, mission statements, identifying strategy, deliverables, work breakdown structure (wbs), plan types, dependencies, PERT, critical path management (cpm), cost terminology, the project manager, report writing, manual methods, resource levelling, popular project management systems, quality function deployment and more...
- Risk managementRisk management covers proactive and reactive planning, triggers, monitoring and control, risk combination,
what is risk, core process steps, project life cycle, terminology, cumulative probability graph, modifying plans,
plan types, identifying risk issues, assessing risk, cost model, Monte Carlo distribution, probability density function (PDF), uncertain events, correlated events, budget versus contingency, simple networks, Markov chain and more... - Time managementTime management covers goals, objectives, time logs, filing, delegation, planning, key time destroyers,
prioritising, urgent versus important, typical process, strategies, positive thinking,
mind maps, monochronic and polychronic time, culture,
convergent and divergent thinking, assertiveness, stress and more... - LeadershipLeadership covers definition, the vision, influencing, change, confidence, motivation,
strategy, personality indicators, trust and integrity, empowerment, prioritising, proactivity,
SWOT analysis, strategy, insight, personal direction, the three C’s, being positive, self discipline,
leadership training, meetings and agendas, styles and more... - MotivationMotivation covers performance management, empowerment, relations and needs, integrity and trust,
consequences, positive and negative reinforcement, measurement, feedback, goals, rewards,
appraisals, creativity and labelling, communication, coaching and mentoring, teamwork and self motivation,
insight, intuition, foresight, inspiration and influence and more...
© Copyright 2020 all rights reserved March Limited