PRINCE2 2009 - Plans part 20
of the Cabinet Office under delegated authority from the Controller of HMSO.
The PRINCE2® approach
Prepare the schedule
Define activity sequence
Having identified the activities, their dependencies and estimated their duration and effort, the next task is to determine the optimal sequence in which they can be performed.
This is an iterative task as the assigning of actual resources may affect the estimated effort and duration.
The amount of time that an activity can be delayed without affecting the completion time of the overall plan is known as the float (sometimes referred to as the slack).
Float can either be regarded as a provision within the plan, or as spare time.
The critical path(s) through the diagram is the sequence of activities that have zero float.
Thus, if any activity on the critical path(s) finishes late, then the whole plan will also finish late (for example, if task 4 in the diagram is delayed, then completion of the plan will be delayed).
Identifying a plan’s critical path enables the Project Manager to monitor those activities:
- That must be completed on time [see 'The Complete Time Management package'] for the whole plan to be completed to schedule
- That can be delayed for a time period if resources need to be re-allocated to catch up on missed activities.
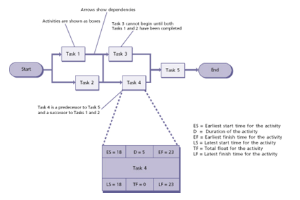
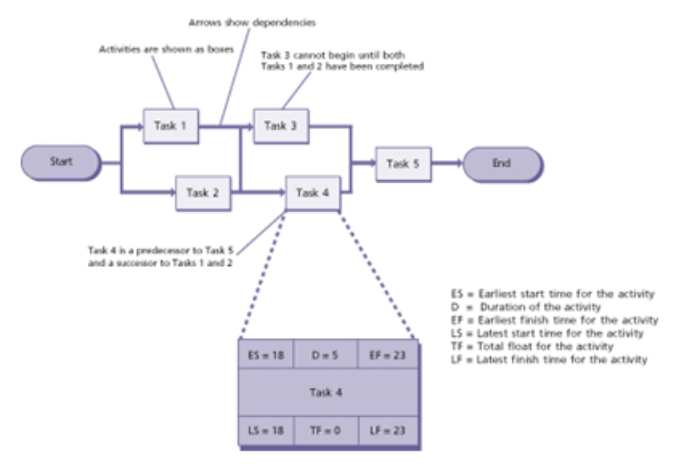
An activity-on-node diagram (sometimes called an arrow diagram) can be used to schedule dependent activities within a plan.
It helps a Project Manager to work out the most efficient sequence of events needed to complete any plan and enables the creation of a realistic schedule.
The activity-on-node diagram displays interdependencies between activities through the use of boxes and arrows.
Arrows pointing into an activity box come from its predecessor activities, which must be completed before the activity can start.
Arrows pointing out of an activity box go to its successor activities, which cannot start until at least this activity is complete.
A simple activity-on-node diagram is shown in the diagram.
PRINCE2® is a Registered Trade Mark of the Office of Government Commerce in the United Kingdom and other countries.
Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 - 2005 edition
Managing successful Projects with PRINCE2 – 2009 edition
Directing Projects with PRINCE2.
plus:
The Complete Project Management package.
And much more besides - at a fantastic price.